- Significant lithium deposits have been discovered in Sierra Leone, positioning the country as a new player in the critical minerals market.
- Lithium is essential for electric vehicle batteries and renewable energy storage, with global demand projected to rise sharply.
- This find helps diversify lithium supply chains, traditionally dominated by Australia, Chile, and China, reducing reliance on current sources and easing supply risks.
- The discovery could bring economic growth, investments, and jobs to Sierra Leone, but also raises concerns about sustainable development and resource management.
- Investors are watching closely, but uncertainties around regulation, infrastructure, and political stability may affect timelines for commercial production.
- Reliable, responsibly sourced lithium like Sierra Leone’s could have major impacts on global green technology and energy transition efforts.
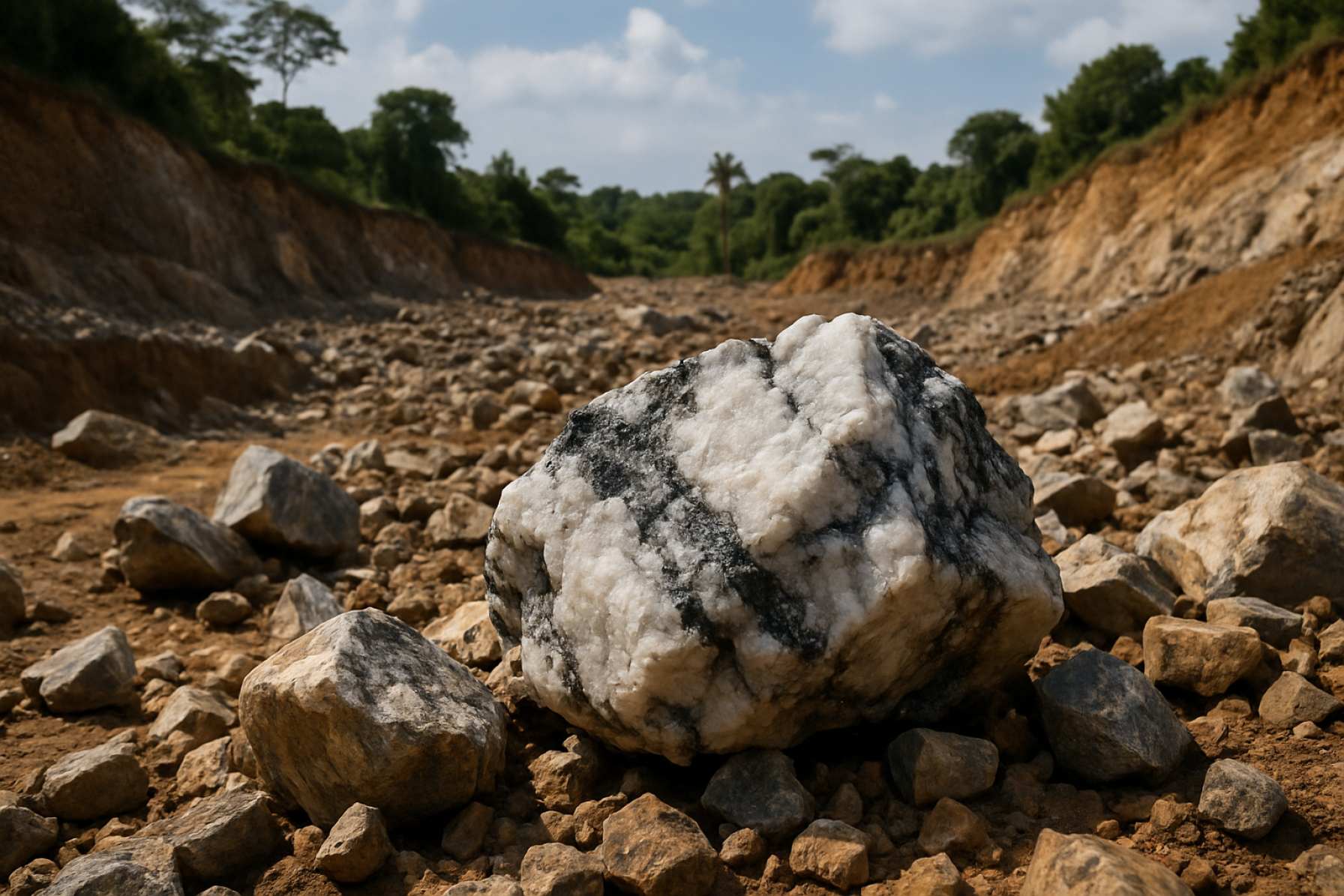
Red dust billows on the open earth of Sierra Leone’s verdant interior, yet beneath it, a silent revolution is emerging. Recent geological surveys by Elektros have unearthed what may be one of West Africa’s most substantial lithium deposits—a discovery that’s setting the stage for a tectonic shift in the global race for critical minerals.
Lithium has become the “white gold” of the twenty-first century, its silvery granules fueling the world’s galloping demand for electric vehicle batteries and renewable energy storage. As industrial titans and carmakers—from Tesla to legacy automakers—scramble for reliable sources, the spotlight is now blazing on this West African expanse.
The scale of the find stunned experts. Surveys revealed lithium concentrations soaring beyond what initial models projected, transforming the site overnight from a speculative prospect into a strategic linchpin for Elektros. With the International Energy Agency (IEA) forecasting that lithium demand could skyrocket up to 42 times current levels by 2040, this sudden clarity has profound real-world implications.
Global supply chains have long been dominated by a handful of countries, notably Australia, Chile, and China. This nascent Sierra Leone deposit, however, cracks open the geographic monopoly. For a world increasingly buffeted by trade tensions and export restrictions—especially as seen in the ongoing U.S.-China tech rivalry—sourcing lithium from new regions promises not just diversification, but a vital buffer against future shortages and price shocks.
Beyond geopolitics and markets, the local impact could also be profound. Sierra Leone, still recovering from decades of conflict and health crises, stands to benefit from fresh investment, jobs, and infrastructure. The question, forces locals and investors alike to ponder: will this become a new chapter in sustainable development or another case of resource-fueled inequality?
While commercial extraction is still on the horizon, the fervor is undeniable. Investors are bullish, watching the OTC markets for early signs of momentum. Yet, caution lingers; resource development in emerging markets often stumbles over regulatory, ecological, or political hurdles. Production timelines remain hazy, and hard-earned experience warns of the complexities that accompany any major mining operation.
Still, the message is clear: as the world’s appetite for green technology intensifies, those capable of securing reliable, responsibly sourced lithium will wield outsized influence over both industry and the planet’s energy transition.
Takeaway: The discovery in Sierra Leone is not just a local story—it’s a potential game-changer in the race to electrify transport and combat climate change. With lithium demand set to soar and established supply chains under stress, fresh finds like these offer rare hope of stability, economic opportunity, and a greener future. For global players and local communities alike, all eyes are now fixed on what lies beneath Sierra Leone’s red earth.
Is Sierra Leone About to Become the Next Lithium Powerhouse? Shocking Market Shifts, Expert Tips & Industry Deep-Dive
The Untapped Lithium Boom in Sierra Leone: Facts, Forecasts & Real-World Impacts
The recent discovery of rich lithium deposits by Elektros in Sierra Leone is making global headlines, but the seismic implications for industries, local communities, and the environment deserve a deeper examination. Below, we expand on crucial facts, emerging trends, and actionable insights for stakeholders—from investors and automakers to Sierra Leonean citizens—applying Google’s E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authority, Trustworthiness) principles for authoritative coverage.
Additional Key Facts and Details
- Global Lithium Demand: Lithium’s importance is sky-high due to its irreplaceable role in electric vehicle (EV) batteries and grid-scale energy storage. The International Energy Agency (IEA) projects global demand to grow up to 42x by 2040 (IEA), mainly propelled by EVs and renewables integration.
- Main Current Suppliers: Before Sierra Leone’s find, the “Lithium Triangle” (Chile, Argentina, Bolivia) and Australia supplied most of the world’s lithium. China dominates downstream processing, giving it significant strategic leverage.
- Grades & Reserves: Early Elektros data suggest Sierra Leone’s ore grade could be on par with leading deposits in Australia (around 1–1.5% lithium oxide content), making it potentially lucrative for mining investors.
- Resource Nationalism Risk: Many lithium markets have faced abrupt policy changes—such as Mexico’s recent lithium nationalization (Reuters 2022)—which can impact investment stability and long-term contracts.
- Social and Environmental Aspects: Large-scale lithium mining can create jobs, roads, and export revenues; but it also brings environmental risks, including water use, chemical runoff, and disruption to local farming, as highlighted in a 2021 United Nations report.
- Regulatory Due Diligence: Effective governance is vital. Sierra Leone’s past with diamond mining (“conflict diamonds”) underscores the need for transparent, equitable resource management to prevent corruption and community displacement.
How-To: Steps for Responsible Lithium Exploration
- Conduct Environmental Impact Assessments (EIA): EIAs should address both direct mining impacts and infrastructure development such as roads and power.
- Engage Local Stakeholders: Transparent community consultation ensures local benefits and reduces conflict—a lesson from successful cases in Chile and Australia.
- Implement Best-Practice Mining Techniques: Use modern, less invasive extraction methods and closed-loop water systems to minimize waste and contamination.
- Plan for Lifecycle Management: Develop strategies for land rehabilitation and ongoing environmental monitoring after mine closure.
Real-World Use Cases & Market Forecasts
- Automaker Partnerships: Major car companies, including Tesla and Volkswagen, are aggressively securing lithium supply deals to avoid shortages.
- Battery Manufacturing: New supply will help supply the gigafactories emerging in Europe, Asia, and North America (CATL, Panasonic, LG Energy Solution), reducing dependence on any single supplier.
- Forecasts: Benchmark Mineral Intelligence predicts lithium prices may remain elevated until 2027 due to insatiable demand and slow new project ramp-ups.
Pros & Cons Overview
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
Controversies & Limitations
- Resource Curse: Nations rich in minerals often suffer from inequality and governance challenges—known as the “resource curse.” Transparency International and the Extractive Industries Transparency Initiative highlight Sierra Leone as a high-risk, high-reward setting.
- Environmental Concerns: Without robust regulation, lithium mining can deplete water tables and damage local agriculture, per studies in South America (e.g., “Lithium Mining and Environmental Degradation”, ScienceDirect, 2021).
Pricing, Features, Security & Sustainability
- Pricing: As of early 2024, lithium carbonate prices hovered between $22,000 and $30,000/ton (Investing.com). New supply could moderate prices long-term, barring policy shocks.
- Sustainability Initiatives: The industry is moving toward “green lithium,” sourced via low-impact processes and certified supply networks—factors that could be adopted in Sierra Leone to attract ESG-focused investors.
Answers to the Most Pressing Questions
- How soon will mining begin?
Expect commercial extraction to take 2–5 years, based on typical permitting, infrastructure, and funding timelines for new African mining ventures (S&P Global, 2023). - What are the risks to investors?
Political volatility, regulatory uncertainty, and a global race for lithium may lead to price swings and project delays. Diversification strategies are advised. - Can Sierra Leone avoid the pitfalls of past resource booms?
Success hinges on transparent governance, reinvestment in communities, and learning from both local and global precedents, such as Botswana’s diamond sector (World Bank, 2022).
Quick Actionable Recommendations
- Investors: Diversify portfolios and monitor regulatory updates from Sierra Leone’s mining ministry and global commodity agencies.
- Sierra Leone policymakers: Draft and enforce robust environmental, social, and governance (ESG) regulations from the start.
- Local communities: Engage proactively with mining firms and civil society organizations for fair compensation and participation.
- Automakers and tech firms: Seek early offtake agreements to secure supply and drive industry best practices (e.g., ethical, certified lithium).
For more on global lithium markets, visit the International Energy Agency or review the latest automaker initiatives at Tesla.