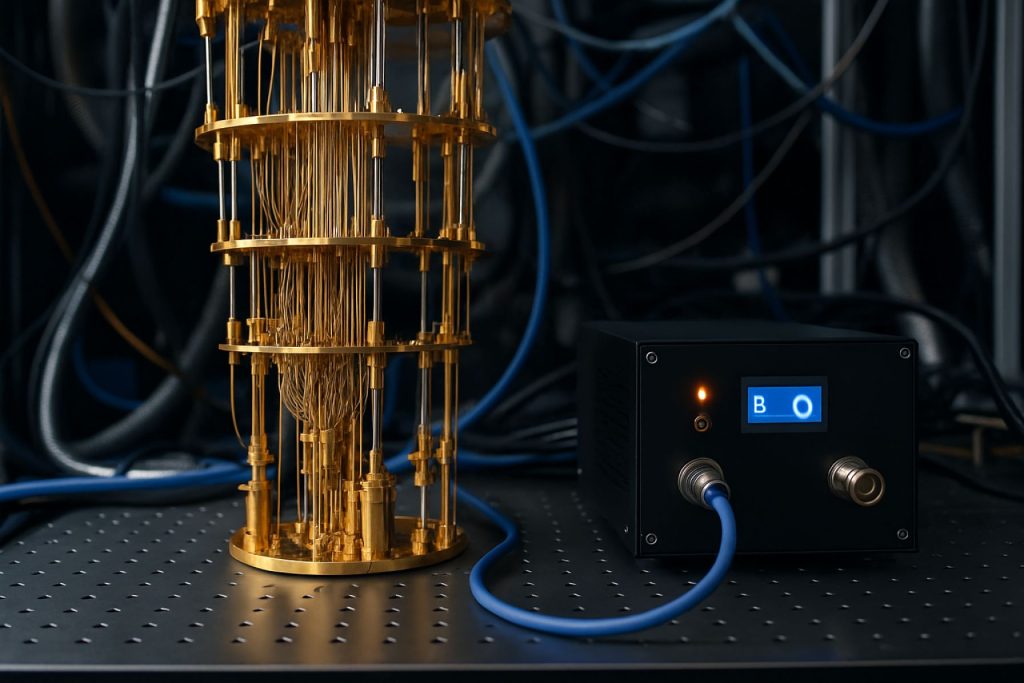
Quantum Computing
Quantum computing is an area of computation that utilizes the principles of quantum mechanics to process information. Unlike classical computers, which use bits as the smallest unit of data (representing either a 0 or a 1), quantum computers use quantum bits, or qubits. Qubits can exist in multiple states simultaneously due to the phenomenon known as superposition. This enables quantum computers to perform complex calculations at much higher speeds than classical computers for certain problems.Another key principle of quantum computing is entanglement, where qubits become interdependent in such a way that the state of one qubit can be dependent on the state of another, regardless of the distance separating them. This allows for more intricate processing and faster information transfer.Quantum computing has the potential to revolutionize various fields, including cryptography, optimization problems, drug discovery, and more, by solving problems that are infeasible for classical computers within a reasonable timeframe. However, it is still a developing technology with many technical challenges to overcome before it becomes widely practical.