Revolutionizing Gastrointestinal Surgery: How Endoluminal Robotics Will Transform Patient Outcomes and Market Dynamics in 2025 and Beyond. Explore the Breakthroughs, Market Forecasts, and Strategic Opportunities Shaping the Next Era of Minimally Invasive Care.
- Executive Summary: Key Insights and 2025 Highlights
- Market Overview: Defining Endoluminal Robotics in GI Surgery
- Current Market Size and 2025–2030 Growth Forecast (CAGR: 18–22%)
- Technology Landscape: Leading Platforms, Innovations, and R&D Pipeline
- Competitive Analysis: Major Players, Startups, and Strategic Alliances
- Clinical Applications: Expanding Indications and Patient Impact
- Regulatory and Reimbursement Trends: Global Perspectives
- Investment and Funding Landscape: Recent Deals and Future Hotspots
- Challenges and Barriers: Technical, Clinical, and Market Adoption
- Future Outlook: Disruptive Trends and Strategic Recommendations for 2025–2030
- Sources & References
Executive Summary: Key Insights and 2025 Highlights
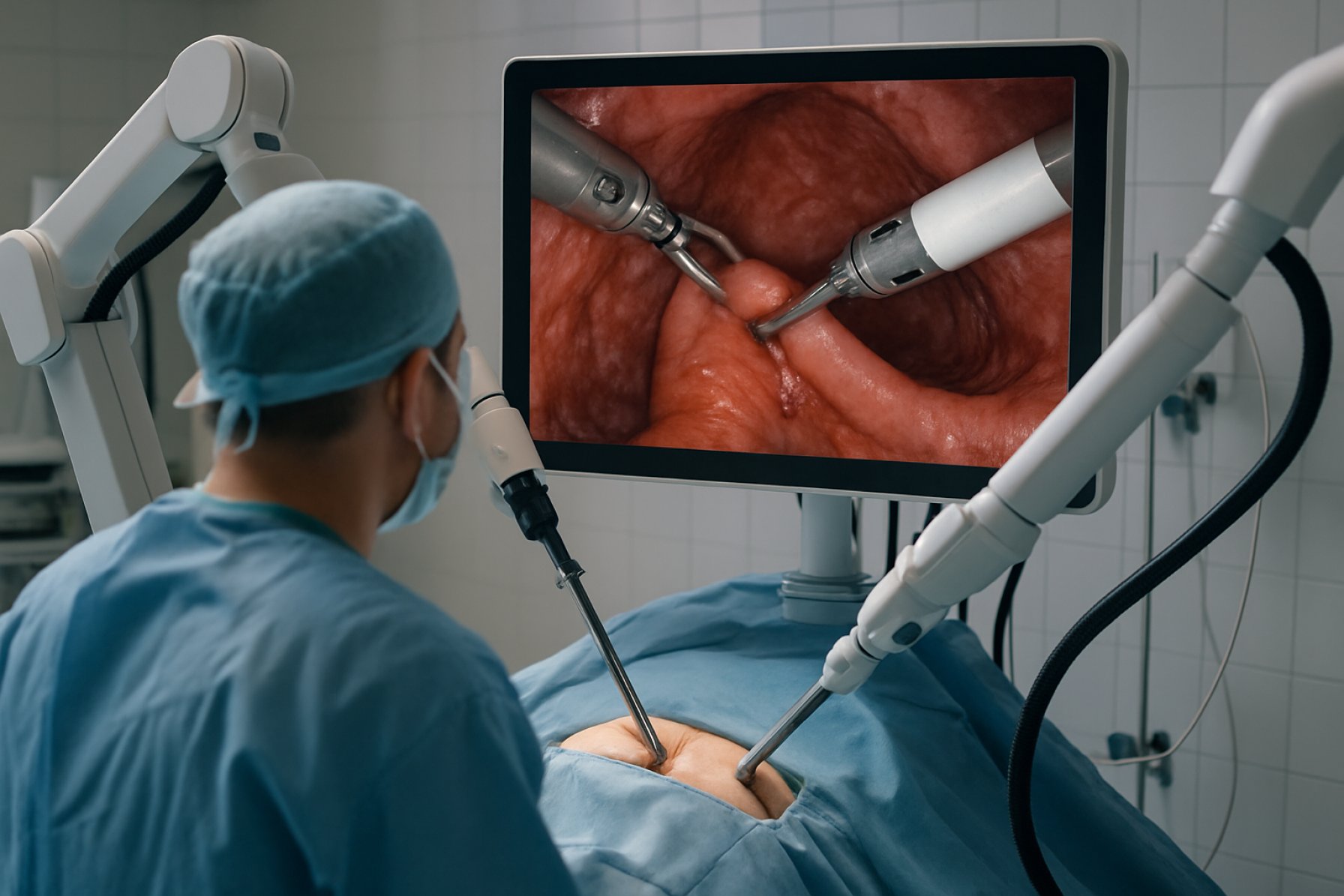
Endoluminal robotics for gastrointestinal (GI) surgery represents a transformative advance in minimally invasive procedures, leveraging robotic platforms to perform complex interventions entirely within the lumen of the GI tract. In 2025, the field is characterized by rapid technological innovation, increased clinical adoption, and expanding indications, driven by the pursuit of improved patient outcomes and procedural efficiency.
Key insights for 2025 highlight the maturation of endoluminal robotic systems, with several platforms achieving regulatory milestones and entering broader clinical use. Notably, companies such as Intuitive Surgical, Inc. and Medtronic plc have advanced their portfolios to include flexible, miniaturized robotic devices tailored for endoluminal access. These systems enable precise dissection, suturing, and tissue manipulation, reducing the need for open or laparoscopic surgery in select GI indications.
Clinical data from leading centers, including those affiliated with the Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons (SAGES), demonstrate that endoluminal robotics can lower complication rates, shorten hospital stays, and accelerate patient recovery compared to conventional techniques. In 2025, the most common applications include endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD), full-thickness resection, and complex polypectomy, with ongoing trials exploring use in bariatric and anti-reflux procedures.
Market dynamics in 2025 are shaped by growing surgeon familiarity, improved training programs, and the integration of artificial intelligence for enhanced navigation and decision support. Strategic partnerships between device manufacturers and healthcare systems are accelerating adoption, while reimbursement frameworks are evolving to recognize the value of robotic endoluminal interventions.
Looking ahead, the field is poised for further expansion as next-generation platforms incorporate haptic feedback, advanced imaging, and remote operation capabilities. The convergence of robotics, digital health, and precision endoscopy is expected to unlock new therapeutic possibilities and set new standards for GI care.
Market Overview: Defining Endoluminal Robotics in GI Surgery
Endoluminal robotics represents a transformative advancement in gastrointestinal (GI) surgery, offering minimally invasive solutions for a range of digestive tract disorders. Unlike traditional open or laparoscopic procedures, endoluminal robotic systems are designed to operate entirely within the lumen of the GI tract, utilizing flexible, miniaturized robotic instruments that are introduced via natural orifices. This approach aims to reduce patient trauma, shorten recovery times, and minimize complications associated with external incisions.
The market for endoluminal robotics in GI surgery is shaped by the growing prevalence of GI diseases, such as colorectal cancer, polyps, and early-stage tumors, which require precise and effective intervention. The demand for less invasive procedures has driven innovation among medical device manufacturers, leading to the development of advanced robotic platforms that enhance the dexterity, visualization, and control available to surgeons. Notable systems in this space include the Ion Endoluminal System from Intuitive Surgical, Inc. and the Hugo™ Robotic-Assisted Surgery System by Medtronic plc, both of which are designed to facilitate complex endoluminal procedures with enhanced precision.
Key drivers of market growth include technological advancements in robotics, such as improved haptic feedback, high-definition 3D imaging, and AI-assisted navigation. These features enable more accurate targeting and resection of lesions, particularly in anatomically challenging locations within the GI tract. Additionally, the integration of robotics with endoscopic techniques is expanding the therapeutic possibilities for conditions that were previously managed with more invasive surgery.
Regulatory approvals and clinical adoption are also influencing the market landscape. Agencies such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) are increasingly evaluating and approving robotic systems for endoluminal use, reflecting growing confidence in their safety and efficacy. As healthcare providers seek to improve patient outcomes and operational efficiency, the adoption of endoluminal robotics in GI surgery is expected to accelerate, positioning this technology as a cornerstone of future minimally invasive interventions.
Current Market Size and 2025–2030 Growth Forecast (CAGR: 18–22%)
The global market for endoluminal robotics in gastrointestinal (GI) surgery is experiencing rapid expansion, driven by technological advancements, increasing adoption of minimally invasive procedures, and a growing prevalence of GI disorders. As of 2025, the market is estimated to be valued at approximately USD 600–700 million, with North America and Europe leading in terms of adoption, followed by Asia-Pacific, where healthcare infrastructure modernization is accelerating uptake.
Endoluminal robotic systems are designed to enhance precision, dexterity, and visualization during complex GI interventions, such as polypectomies, submucosal dissections, and tumor resections. The integration of robotics into endoscopic platforms is being pioneered by companies like Intuitive Surgical, Inc., Medtronic plc, and Olympus Corporation, all of which are investing heavily in R&D and clinical validation.
From 2025 to 2030, the endoluminal robotics market for GI surgery is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 18–22%. This robust growth is attributed to several factors:
- Rising incidence of colorectal and gastric cancers, fueling demand for advanced surgical solutions.
- Expanding indications for endoluminal robotic procedures, including bariatric and anti-reflux surgeries.
- Favorable reimbursement policies and increasing surgeon training programs, particularly in developed markets.
- Continuous product innovation, such as flexible robotic platforms and AI-assisted navigation, by leading manufacturers.
Emerging players and academic collaborations are also contributing to market dynamism, with new systems entering clinical trials and regulatory pathways. For instance, Medrobotics Corporation and Asensus Surgical, Inc. are expanding their portfolios to address unmet needs in GI endoluminal interventions.
Looking ahead, the market’s trajectory will be shaped by ongoing clinical evidence, regulatory approvals, and the pace of hospital adoption. By 2030, the global market size is expected to surpass USD 1.5 billion, with Asia-Pacific anticipated to register the fastest CAGR due to rising healthcare investments and a large patient base.
Technology Landscape: Leading Platforms, Innovations, and R&D Pipeline
The technology landscape for endoluminal robotics in gastrointestinal (GI) surgery is rapidly evolving, driven by advances in miniaturization, flexible robotics, and real-time imaging. Leading platforms are being developed to address the limitations of traditional endoscopy and laparoscopic surgery, offering enhanced dexterity, precision, and access to previously challenging anatomical sites within the GI tract.
Among the most prominent systems is the FLEX Robotic System by Intuitive Surgical, Inc., which utilizes a flexible robotic endoscope to navigate complex luminal pathways. The system is designed for transoral and transanal procedures, providing surgeons with improved control and visualization. Another notable platform is the Flex® Robotic System from Medrobotics Corporation, which has received regulatory approvals in multiple regions and is being adopted for minimally invasive colorectal and upper GI surgeries.
Innovation in this field is also marked by the development of soft robotics and magnetically actuated devices. Research groups, such as those at Imperial College London’s Robotics Laboratory, are pioneering soft, flexible robots capable of navigating tortuous GI anatomy with minimal trauma. These systems often integrate advanced imaging modalities, such as high-definition 3D visualization and augmented reality overlays, to enhance intraoperative guidance.
The R&D pipeline is robust, with several companies and academic consortia focusing on next-generation platforms. Auris Health, Inc. (a subsidiary of Johnson & Johnson) is developing robotic endoluminal systems that combine AI-driven navigation with precision instrumentation for early cancer detection and therapeutic interventions. Meanwhile, Olympus Corporation is investing in robotic-assisted endoscopy platforms, aiming to expand the range of treatable GI conditions and improve procedural outcomes.
Collaborative efforts between industry and academia are accelerating the translation of novel robotic concepts into clinical practice. The focus is on improving haptic feedback, miniaturizing actuators, and integrating AI for autonomous or semi-autonomous navigation. As these technologies mature, endoluminal robotics is poised to transform GI surgery by reducing invasiveness, shortening recovery times, and expanding the therapeutic possibilities for complex GI diseases.
Competitive Analysis: Major Players, Startups, and Strategic Alliances
The landscape of endoluminal robotics for gastrointestinal (GI) surgery is rapidly evolving, marked by the presence of established medical device companies, innovative startups, and a growing number of strategic alliances. Major players such as Intuitive Surgical, Inc. and Olympus Corporation have leveraged their expertise in minimally invasive and robotic-assisted surgery to develop platforms that enable advanced endoluminal procedures. Intuitive Surgical, known for its da Vinci systems, has expanded its research into flexible robotics for natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery (NOTES), while Olympus has introduced endoscopic platforms with robotic enhancements to improve precision and control.
Startups are driving innovation in this sector by focusing on highly specialized robotic systems tailored for GI applications. Medtronic plc has made significant investments in robotic endoscopy, notably through its acquisition of Digital Surgery and partnerships to develop AI-driven navigation for endoluminal procedures. Meanwhile, companies like EndoMaster Pte Ltd and Anthropic (if involved in medical robotics) are developing novel robotic platforms that offer enhanced dexterity, haptic feedback, and improved ergonomics for complex GI interventions.
Strategic alliances are a key feature of the competitive landscape, as established firms seek to accelerate innovation and market entry by partnering with technology startups, academic institutions, and healthcare providers. For example, Johnson & Johnson (through its Ethicon division) has formed collaborations with robotics companies and research centers to co-develop next-generation endoluminal systems. Similarly, Smith+Nephew and Boston Scientific Corporation have entered into joint ventures and licensing agreements to expand their portfolios in robotic GI surgery.
The competitive dynamics are further shaped by regulatory milestones and clinical trial outcomes, with companies racing to secure approvals and demonstrate superior clinical efficacy. As the field matures, the convergence of robotics, artificial intelligence, and advanced imaging is expected to intensify competition, foster new alliances, and drive the adoption of endoluminal robotics in GI surgery worldwide.
Clinical Applications: Expanding Indications and Patient Impact
Endoluminal robotics are rapidly transforming the landscape of gastrointestinal (GI) surgery by enabling minimally invasive interventions that were previously unfeasible or required open procedures. Initially developed for polypectomy and early-stage tumor resections, these robotic systems are now being applied to a broader range of clinical indications, including complex submucosal dissections, full-thickness resections, and even anastomosis creation within the GI tract. This expansion is driven by advances in robotic dexterity, miniaturization, and real-time imaging integration, which collectively enhance precision and safety during endoluminal procedures.
One of the most significant impacts of endoluminal robotics is the ability to treat early and intermediate GI cancers with organ-sparing techniques. For example, robotic platforms such as the Intuitive Surgical ION and Medtronic Hugo™ RAS System are being evaluated for their ability to perform precise endoscopic submucosal dissections (ESD) and endoscopic full-thickness resections (EFTR) in the esophagus, stomach, and colon. These procedures can reduce the need for open or laparoscopic surgery, minimize postoperative pain, and shorten hospital stays, thereby improving patient quality of life.
Beyond oncologic applications, endoluminal robotics are also being explored for the management of benign GI diseases. For instance, robotic-assisted endoscopic myotomy is emerging as a promising treatment for achalasia and other esophageal motility disorders, offering enhanced control and visualization compared to conventional endoscopy. Additionally, the use of robotic systems in bariatric endoscopy is under investigation, with the potential to perform primary weight-loss procedures and revisions of previous surgeries with greater accuracy and fewer complications.
The patient impact of these expanding indications is substantial. Minimally invasive, organ-preserving approaches can lead to faster recovery, lower complication rates, and reduced healthcare costs. Furthermore, the precision of robotic systems may enable the treatment of lesions in anatomically challenging locations, expanding access to curative interventions for a broader patient population. As clinical trials and real-world studies continue, the role of endoluminal robotics in GI surgery is expected to grow, with ongoing innovation from companies such as Olympus Corporation and Ethicon (Johnson & Johnson MedTech) further driving adoption and improving patient outcomes.
Regulatory and Reimbursement Trends: Global Perspectives
The regulatory and reimbursement landscape for endoluminal robotics in gastrointestinal (GI) surgery is rapidly evolving, reflecting both the technological advancements and the growing clinical adoption of these systems. Regulatory agencies worldwide are adapting their frameworks to address the unique challenges and safety considerations posed by robotic-assisted endoluminal procedures. In the United States, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has established pathways for the clearance and approval of robotic surgical devices, often requiring robust clinical evidence demonstrating safety, efficacy, and substantial equivalence to predicate devices. The FDA’s Breakthrough Devices Program has also facilitated expedited review for innovative endoluminal robotic platforms that address unmet clinical needs in GI surgery.
In Europe, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and national competent authorities oversee the conformity assessment of medical devices under the Medical Device Regulation (MDR 2017/745). The MDR places a strong emphasis on post-market surveillance and clinical data, requiring manufacturers of endoluminal robotic systems to provide comprehensive evidence of performance and safety. The European Commission has also encouraged harmonization of standards to streamline market access across member states.
In Asia-Pacific, regulatory requirements vary significantly. For instance, Japan’s Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) has developed specific guidelines for the approval of robotic surgical devices, focusing on both preclinical and clinical evaluation. China’s National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) has similarly updated its regulatory processes to accommodate the rapid growth of domestic and imported robotic systems.
Reimbursement remains a critical factor influencing the adoption of endoluminal robotics. In the U.S., the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) has begun to recognize certain robotic-assisted GI procedures for reimbursement, though coverage decisions often depend on demonstrated improvements in patient outcomes and cost-effectiveness. European countries typically rely on national health technology assessment (HTA) bodies to evaluate the value proposition of new technologies, which can result in variable reimbursement policies across the region. In Asia, reimbursement pathways are still developing, with pilot programs and selective coverage in countries like Japan and South Korea.
Overall, the global regulatory and reimbursement environment for endoluminal robotics in GI surgery is characterized by increasing scrutiny, a demand for high-quality clinical evidence, and gradual expansion of reimbursement as clinical and economic benefits are demonstrated.
Investment and Funding Landscape: Recent Deals and Future Hotspots
The investment and funding landscape for endoluminal robotics in gastrointestinal (GI) surgery has experienced significant momentum in recent years, reflecting both the maturation of the technology and growing clinical demand. Venture capital and strategic investments have increasingly targeted companies developing flexible, minimally invasive robotic platforms designed for GI interventions, such as polypectomy, submucosal dissection, and full-thickness resections. Notably, the sector has attracted funding from both traditional medtech investors and major industry players seeking to expand their portfolios in digital and robotic surgery.
Recent high-profile deals include substantial Series B and C rounds for startups specializing in flexible robotic endoscopy systems. For example, Medtronic plc has continued to invest in its GI robotics pipeline, following its acquisition of Digital Surgery and partnership with Intuitive Surgical, Inc. to explore next-generation endoluminal platforms. Similarly, Olympus Corporation has increased its commitment to robotic endoscopy, both through internal R&D and strategic investments in emerging companies.
Geographically, North America and Europe remain the primary hotspots for investment, driven by robust healthcare infrastructure, established regulatory pathways, and a high concentration of academic medical centers. However, Asia-Pacific markets, particularly Japan and South Korea, are rapidly emerging as innovation hubs, supported by proactive regulatory agencies and a strong tradition in endoscopic surgery. Olympus Corporation and FUJIFILM Holdings Corporation have both announced new funding initiatives and partnerships in the region to accelerate the development and commercialization of endoluminal robotic systems.
Looking ahead to 2025 and beyond, future investment hotspots are expected to include AI-driven navigation, haptic feedback integration, and cloud-based data analytics for procedural optimization. Investors are also closely watching companies that can demonstrate clear clinical and economic value, particularly those with platforms capable of addressing a broad range of GI pathologies. As reimbursement frameworks evolve and clinical evidence mounts, the sector is poised for continued growth, with strategic acquirers and public market exits likely to shape the next phase of the endoluminal robotics landscape.
Challenges and Barriers: Technical, Clinical, and Market Adoption
Endoluminal robotics for gastrointestinal (GI) surgery represents a transformative approach, offering minimally invasive alternatives to traditional open and laparoscopic procedures. However, the adoption of these technologies faces significant challenges across technical, clinical, and market domains.
Technical Barriers: The development of endoluminal robotic systems is constrained by the need for miniaturization, flexibility, and precise control within the complex and delicate environment of the GI tract. Achieving sufficient dexterity and force transmission in a compact form factor remains a major engineering hurdle. Additionally, integration of high-definition imaging, haptic feedback, and advanced navigation systems is essential for safe and effective operation, but these features increase system complexity and cost. Ensuring device reliability and sterility, especially for reusable components, further complicates design and manufacturing processes. Companies such as Intuitive Surgical, Inc. and Medtronic plc are actively investing in research to address these technical limitations.
Clinical Barriers: Clinically, the adoption of endoluminal robotics is hindered by a lack of long-term outcome data and standardized protocols. Surgeons require extensive training to master the unique skill set demanded by robotic endoluminal procedures, and the learning curve can be steep. There is also variability in patient anatomy and pathology, which can limit the applicability of current robotic platforms. Furthermore, regulatory approval processes, such as those overseen by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and European Medicines Agency (EMA), require robust clinical evidence, which can delay market entry and increase development costs.
Market Adoption Barriers: From a market perspective, the high initial investment and ongoing maintenance costs of robotic systems can be prohibitive for many healthcare institutions. Demonstrating clear cost-effectiveness compared to established techniques is essential for widespread adoption. Reimbursement policies, which vary by country and insurer, may not yet fully recognize or support robotic endoluminal procedures. Additionally, the competitive landscape is evolving, with new entrants and established players vying for market share, leading to uncertainty for hospitals considering long-term investments. Organizations such as Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons (SAGES) are working to develop guidelines and advocate for broader acceptance.
Overcoming these challenges will require continued collaboration among device manufacturers, clinicians, regulatory bodies, and professional societies to ensure that endoluminal robotics can realize its full potential in GI surgery.
Future Outlook: Disruptive Trends and Strategic Recommendations for 2025–2030
The future of endoluminal robotics for gastrointestinal (GI) surgery is poised for significant transformation between 2025 and 2030, driven by rapid technological advancements and evolving clinical needs. Key disruptive trends include the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) for real-time decision support, miniaturization of robotic platforms, and the expansion of teleoperated procedures. AI-powered image analysis and navigation are expected to enhance intraoperative precision, enabling surgeons to identify lesions and anatomical landmarks with greater accuracy. Companies such as Intuitive Surgical, Inc. and Olympus Corporation are already investing in AI-driven endoscopic systems, signaling a shift toward more autonomous and adaptive robotic platforms.
Miniaturization will further enable the development of flexible, soft robotics capable of navigating complex GI anatomies with minimal trauma. This trend is exemplified by research collaborations and prototypes from organizations like Boston Scientific Corporation, which are exploring ultra-thin, steerable robotic endoscopes for both diagnostic and therapeutic interventions. Additionally, the convergence of robotics with advanced imaging modalities—such as high-definition 3D visualization and augmented reality overlays—will likely improve procedural outcomes and reduce learning curves for clinicians.
Teleoperated and remote robotic surgery is another area set for growth, particularly in response to global disparities in specialist access. The development of secure, low-latency communication networks will allow expert surgeons to perform complex GI procedures remotely, expanding access to high-quality care in underserved regions. Initiatives by Medtronic plc and academic partners are already piloting remote robotic endoscopy platforms, laying the groundwork for broader adoption.
Strategic recommendations for stakeholders include investing in cross-disciplinary R&D to accelerate AI and robotics integration, fostering partnerships with regulatory bodies to streamline approval pathways, and prioritizing clinician training programs to ensure safe adoption. Health systems should also evaluate the cost-effectiveness and workflow integration of new robotic platforms, leveraging pilot programs and real-world evidence to guide procurement decisions. As the field evolves, collaboration between industry leaders, healthcare providers, and regulatory agencies will be essential to realize the full potential of endoluminal robotics in GI surgery.
Sources & References
- Intuitive Surgical, Inc.
- Medtronic plc
- Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons (SAGES)
- European Medicines Agency (EMA)
- Olympus Corporation
- Asensus Surgical, Inc.
- Imperial College London’s Robotics Laboratory
- Anthropic
- Smith+Nephew
- Boston Scientific Corporation
- European Commission
- Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA)
- National Medical Products Administration (NMPA)
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS)
- FUJIFILM Holdings Corporation